What is Down Syndrome?
Down syndrome, also called trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by extra genetic material (chromosomes). Chromosomes contain the instructions that determine the inherited characteristics that distinguish one individual from another. Most people have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell. Children with Down syndrome have a third 21st chromosome.
What Causes Down Syndrome?
There are no known causes of Down syndrome. The actions of parents or environmental factors are not known to cause Down sydnrome.
Common Characteristics
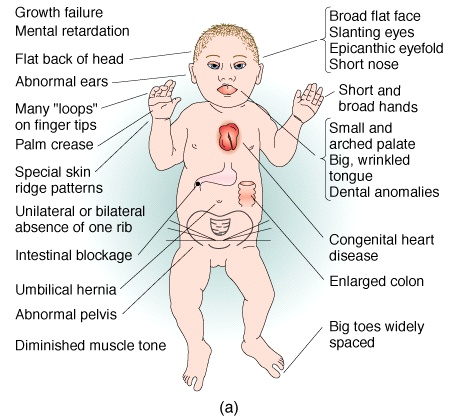
The following characteristics are commonly associated with Down syndrome. Please remember that no two cases of Down syndrome in babies is the same and that not all babies will possess all of these features.
Low Muscle Tone: Babies with Down syndrome have “hypotonia” or low muscle tone. This means that their muscles usually appear relaxed and feel somewhat “floppy”. Low muscle tone will affect the development of skills like rolling over, crawling, standing and walking. Hypotonia will have an effect on feeding. Latching onto a bottle is sometimes difficult and the acceptance of solid foods is can be a chore due to the low muscle tone around the mouth.
Facial Features
Babies with Down syndrome may have some or all of these features:
Nose: The bridge of her nose may be somewhat flatter than usual. Children with Down syndrome often have smaller noses.
Eyes: Eyes may appear to slant upwards and have small folds of skin at the inner corners. The colored part of the eye (the iris) may also have tiny light spots do not affect the baby’s sight. Vision problems are more common in children with Down syndrome than in other children.
Mouth: A baby with Down syndrome may have a small mouth which means the roof of the mouth will be shallow.This in combination with low muscle tone may affect your baby’s ability to keep their tongue inside their mouth. Babies with Down syndrome do not have tongues that are larger than normal.
Teeth:Teeth may come in late. The teeth may also be small, oddly shaped and sometimes out of place. These problems sometimes fix themselves when permanent teeth come in.
Ears: Ears may appear set a little lower on the head and the tops may fold over slightly. Kids with Down syndrome are more prone to ear infections.
Hands and Feet: Hands may be smaller and her fingers shorter. There may also only be one crease across the palm of each hand. The feet usually appear normal, but there may be a gap between the first and second toes.
Skin: Skin can be fair, very sensitive and prone to irritation.
Hair: Children with Down syndrome often have soft, fine, sparse hair.
Chest: The chest may be somewhat funnel shaped or pigeon boned.
Height: Normal growth and development is usually slowed. Most affected children never reach average adult height.
Intellectual Disability
Intellectual disability in children with Down syndrome can be mild, moderate or severe. Some children never learn to speak. Others talk (and often love to talk). Many can learn to read and write. Most of these boys and girls are very friendly and affectionate and behave well with people who treat them well. Even children who are more severely affected, with help and good teaching, usually learn to take care of their basic needs and to help out with simple work. They can live fairly normally with their families and communities.
Medical Problems Common in Children with Down Syndrome
- Heart defects present from birth.
- Problems with the blockage of the digestive tract.
- Cancer of the blood (leukemia) is more prevalent in children with Down syndrome.
- Unstable joints.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for Down syndrome. Early intervention programs (like those offered at The Inspiration Center) can help provide parents with realistic expectations and to facilitate growth and development in a child with this condition.